Oxygen Interface
https://tu-plogan.github.io/source/r_oxygen-interface.html
An introduction to the main components of the Oxygen interface.
When you open Oxygen XML Editor, you will see the editor in Text Editing Mode, as below. If instead you see the Welcome dialogue box, uncheck Show at startup in the lower left corner and click Close.
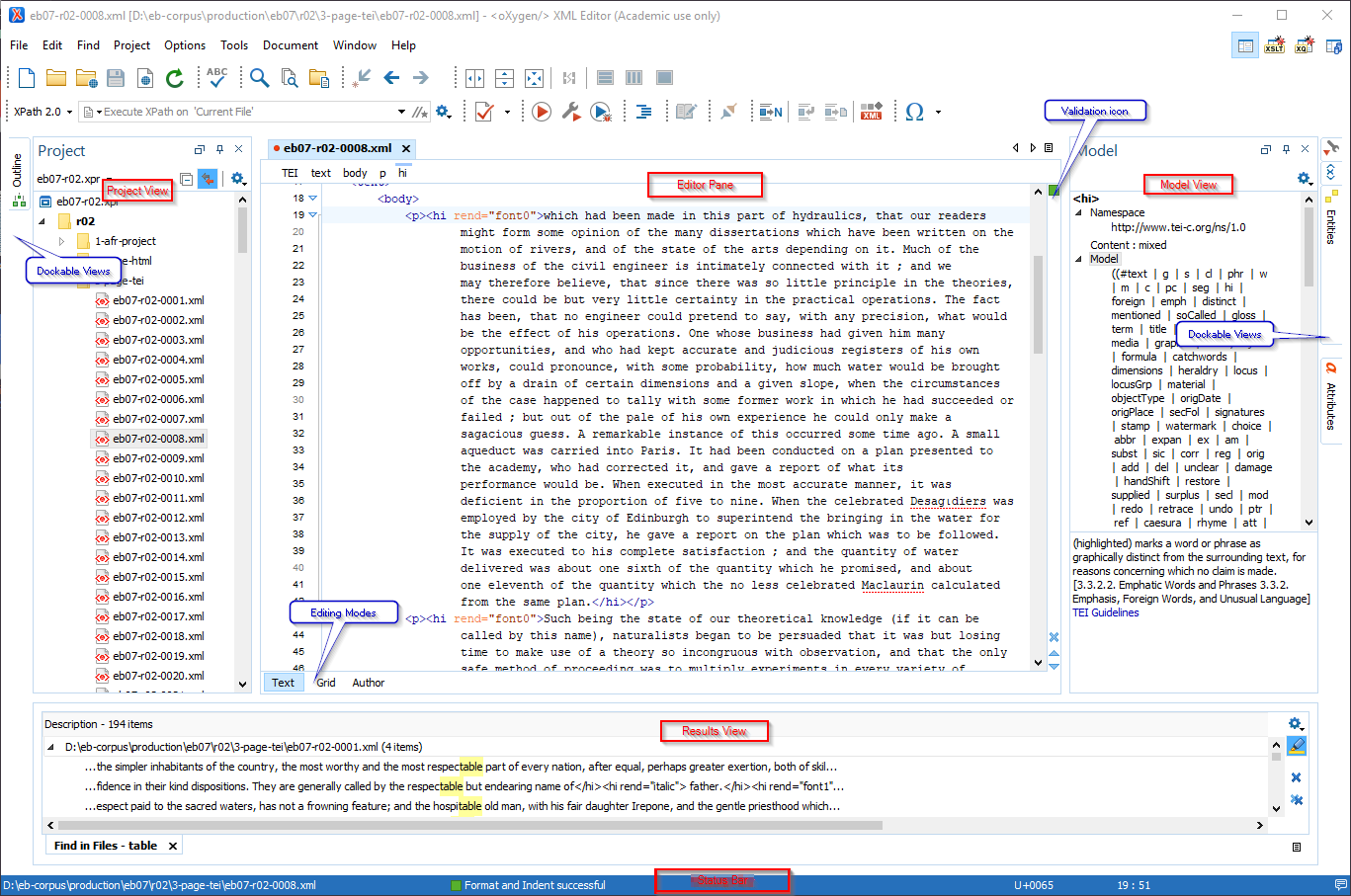
Begin by familiarizing yourself with the different sections of the Oxygen interface.
- The Menus at the top are similar to other Windows programs, although the options are different.
- The Toolbars below the Menus provide easy access to common functions. They are also fully configurable by right-clicking in an empty part of the menu bars. The image above contains several menus in addition to the default menus.
- The Editor Pane in the center of the interface allows you to work with files in three different Editing Modes, which you select at the bottom of the pane. Text mode is shown, where you can see the coding directly. Author mode provides something similar to a WYSIWYG interface, where you can see an approximation of the final appearance of page, but it is less convenient to work in when editing or proofing documents.
- The Project View in the left-hand pane is one of several different views that you can dock in place. Project View lets you see all of the files and folders in the current xml-project. By right-clicking a file or folder, you can also check validation and run transformation scenarios on the selected files.
- The Model View on the right is, again, one of several different helper views that can be docked in place or hidden from view. The Model View shows the definition of the XML element at the cursor placement. Additional views can be seen by clicking the tabs on the right.
- The Results View displays the messages generated as a result of user actions such as validations, transformations, search operations, and others. Each message is a link to the location related to the event that triggered the message. Double-clicking a message opens the file containing the location and positions the cursor at the location offset.
- The blue Status Bar at the bottom of the window includes the following information, in the order it is displayed from left to right:
- The path of the current document.
- Information about the most recent operation, such as formatting or validating.
- The Unicode value for the character directly to the right of the current cursor position
- The status of the current document. The status of Modified is displayed for documents that have not yet been saved. Otherwise, this section is left blank.
- In Text editing mode, the current line and character position is displayed.